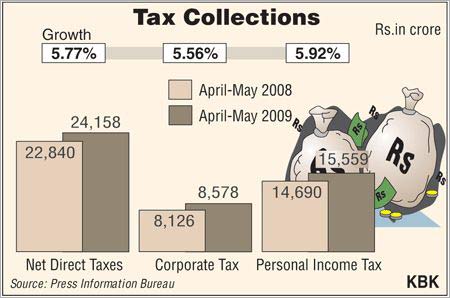
Tax Payment Guide on Various Sources of Income in India
Online Income Tax Rules
When earning income online through blogging, freelancing or any other digital means, this income will be taxed under the ‘Income from Other Sources’ category as per Indian Income Tax laws. Some key aspects related to tax treatment of online income are: Gross total income is calculated by deducting all business expenses like website hosting, domain registration, software costs etc. from the total revenue earned. Depreciation on assets like computer, camera etc. can also be deducted. Tax deductions under sections like 80C, 80D etc. are also allowed to be claimed on the total income amount. The final taxable income is what the slab rates are applied on to calculate the tax liability. It is advised to take help from a chartered accountant to properly account for all income and expenses, claim deductions and file ITR accurately.
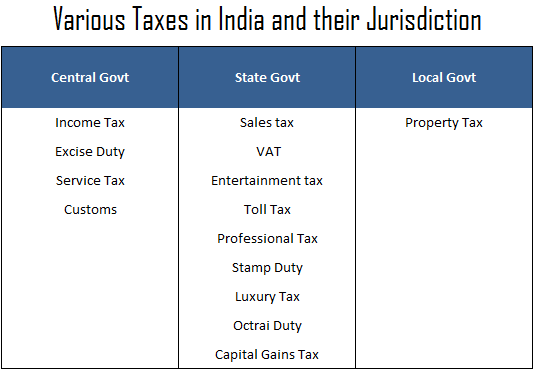
Calculating Tax on Multiple Income Sources
When an individual earns income from multiple avenues like salary, business, rentals, dividends etc., the tax treatment is as follows: All sources of income are categorized under the major heads namely salary, house property, profits & gains of business/profession, capital gains and income from other sources. The gross total income is calculated by aggregating income from all sources. Standard deduction of Rs. 50,000 is allowed under section 16(ia). Deductions available under sections like 80C, 80D, 80G, 24(b), etc. up to a prescribed limit can be claimed to arrive at the total income. The applicable tax rate is determined based on the slab rates for the total income amount. Taxes are paid accordingly after claiming any tax rebates.
Filing Income Tax Return
It is mandatory for all individuals whose total income exceeds the basic exemption limit to file an ITR by the due date, which is typically July 31 for the previous financial year. The ITR includes disclosing income from all sources along with claiming deductions. Depending on the total income , individuals may have to pay advance tax in instalments during the year. For smooth ITR filing, it is recommended to maintain documents containing proof of income, TDS certificates, interest receipts, Form 16, etc. throughout the year. Various e-filing websites supported by the Income Tax Department like www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in can be used for easy and accurate ITR filing.
Tax Compliance for Non-Resident Individuals
For an Indian citizen living abroad or a foreign national, the global income earned is considered for Indian tax purposes based on his resident status:
- Resident but not ordinarily resident (RNOR): Income earned in India and from a business controlled in India is taxable in India.
- Non-resident: Only income earned/accrued in India through a business controlled from India or from any other sources in India is taxable in India.
It is important for NRIs to file ITR by the due date by disclosing their worldwide incomes and claim reliefs to pay correct taxes in India.
Key Takeaways
In summary, income from all sources has to be declared in the ITR. The** applicable tax rates** are determined basis the total taxable income after claiming all available deductions and exemptions. Proper tax compliance ensures correct taxes are paid on time every year. It is recommended to seek expert support to handle tax filing compliance efficiently.