Understanding the Big Bang Theory
The big bang theory has long been a source of mystery and debate. What is often misunderstood is that the theory itself does not attempt to explain how the universe was created. This article aims to provide a comprehensive yet accessible overview of what the big bang theory is truly about based on current scientific consensus.
Tracing the Evolution of the Universe
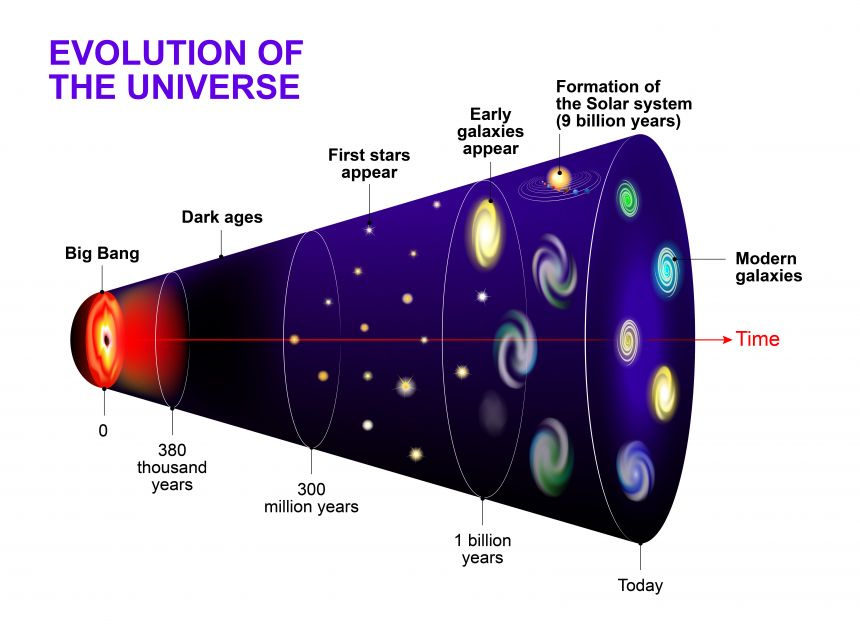
The big bang theory utilizes various lines of observational evidence and scientific theories that have stood up to rigorous testing to reconstruct how the universe has evolved over time. By looking at phenomena like the expansion of space, the abundance of elemental isotopes, and the leftover cosmic microwave background radiation, scientists have been able to reliably trace the history of the universe backwards to a point approximately 13.8 billion years ago when it was intensely hot and dense.
Mapping the Early Stages of Cosmic Evolution
As scientists push the boundary of how far back they can see, new space telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope promise to reveal even more details about the very first galaxies and stars that formed in the aftermath of the big bang. By studying ancient light from increasingly distant cosmic epochs, astronomers hope tomap out the initial morphological and chemical transitions that the universe underwent as it first cooled and condensed over its early history.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/131226922_HighRes-resize-56a72be03df78cf77292fbe1.jpg)
Investigating the Frontiers of Theoretical Cosmology
However, no matter how precisely we can measure the state of the universe billions of years ago, there are inherent limitations to how far the big bang theory can stretch. As the universe is rewound to higher densities and temperatures nearing the Planck scale, the reigning laws of physics like general relativity break down and our standard theories become inapplicable.
Pushing at the Boundaries of Knowledge
At the boundary known as the Planck epoch, less than one trillionth of a second into the proposed hot dense phase, scientists believe new quantum gravitational effects must dominate but remain mathematically intractable with our current tools. It is here that theorists enter the realm of well-motivated but uncertain speculations involving concepts like cosmological inflation, string theory, loop quantum gravity, and more.
Clarifying Common Misconceptions
Given its widespread recognition as a theory of cosmic origins, it is understandable why the big bang theory is commonly misinterpreted as explaining the beginning of time itself. However, this fails to appreciate the clear conceptual distinctions in the types of questions addressed by science.
Distinguishing Cosmology from Metaphysics
Cosmology based on the big bang provides a well-tested framework for describing physical processes in the observable universe from around 10^-43 seconds after an initial hot, dense state. But it makes no assertion about what triggered or came before this early period, which belongs to the separate realm of metaphysical philosophy rather than empirical science based on measurement and falsifiability.
Filling Knowledge Gaps with Careful Speculation
While firm science stops at the Planck scale, theorists do put forth various speculative scenarios to potentially account for how conditions necessary for the big bang itself could have been set up, like the existence of higher dimensional objects or pre-existing cycles of contraction and expansion.
Approaching the Unknown with Caution
However, such ideas remain squarely in the domain of conjecture since any mechanisms proposed would necessarily operate far beyond where experiments can test them. Any testable implications these conjectures might have for observable phenomena today are also largely absent. For now, the ultimate question of the deep past before 10^-43 seconds seems destined to remain an open mystery.
Looking to the Future of Cosmology
Even with its inherent limitations in addressing origins, the big bang theory has revolutionized our vision of cosmic evolution and transformed cosmology into a precise science. As observational and theoretical advances continue pushing its explanatory coverage further, exciting discoveries no doubt still lie ahead.
New Insights Await from Upcoming Missions
New spaceborne instruments promise breakthroughs like directly imaging exoplanets, reconstructing star formation history across galaxies, and potentially detecting primordial gravitational waves. Meanwhile, experiments at larger particle colliders seek to uncover secrets bridging astrophysics and fundamental interactions. The frontier of cosmology is sure to bring many more consequential revelations in the decades to come.