A Comparison of Persian and Pashto languages
Origins and Evolution
Persian and Pashto originated from a common ancestor language known as Proto-Iranian. This proto-language existed thousands of years ago and eventually diverged into Western Iranian and Eastern Iranian branches. Persian is classified as a Western Iranian language and can trace its roots back to Old Persian. Over time, Old Persian evolved into Middle Persian and then evolved further into Modern Persian. On the other hand, Pashto is an Eastern Iranian language that formed from a mix of Eastern Iranian languages such as Avestan and Bactrian. Both languages have been influenced by geographical factors and neighboring languages during their evolution. For instance, the Proto-Iranian sound shift changed the [b] sound to a [w] sound in Eastern Iranian languages. Additionally, Pashto incorporated some sounds from surrounding Indo-Aryan languages like retroflex consonants. This led to unique letters in the Pashto alphabet like the retroflex consonant ټ.
Linguistic Comparisons
Despite originating from a common root, Persian and Pashto have developed distinct phonological and grammatical systems over millennia. Some notable comparisons:
- Vocabulary: Many basic vocabulary words share cognates between the two languages but have undergone sound shifts. For example, “blood” is xun in Persian and wina in Pashto.
- Consonant Clusters: Pashto allows for consonant pairs that merge to form single sounds, like the letter ځ with a [dz] sound. Persian does not have such clusters.
- Grammar: Pashto grammar is generally more complex than Persian with intricacies like noun classes. For instance, the word for “horse” changes based on gender (aas for male, aspa for female).
- Influence of Other Languages: Persian incorporates more Arabic and Turkic influences while Pashto was impacted mainly by Indic grammar and sounds.
Overall, while related historically, today Persian and Pashto have significant differences in their phonology, vocabulary, and grammatical structures. Their divergent evolution paths have made them distinct languages.
Impact of Geography and Culture
The geographical areas where Persian and Pashto are currently spoken also played a role in their differentiation.
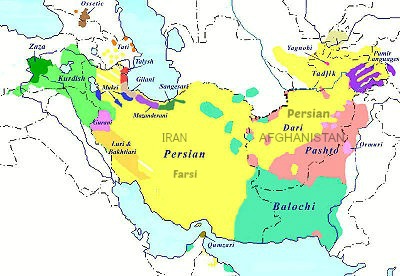
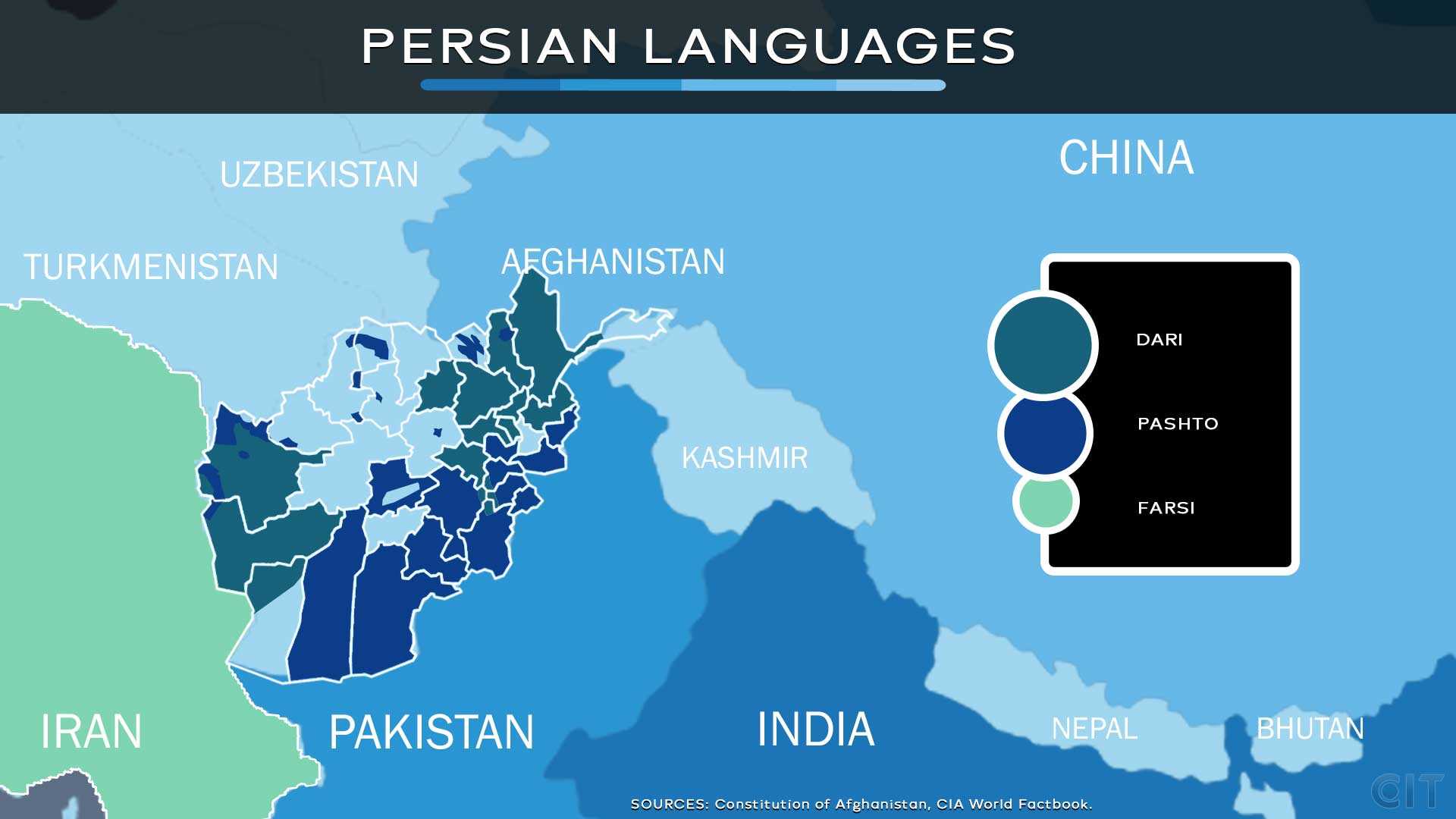
- Regions: Persian is primarily used in Iran, Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Pashto is found mostly in eastern and southern Afghanistan, northwest Pakistan and parts of northern India.
- Neighboring Languages: Persian co-existed with Turkic and Arabic languages. Pashto was neighbor to Indic languages of the Indian subcontinent.
- Ethnicity: Most Persian speakers identify as ethnically Persian while Pashtuns connect their identity more with the Pashtunwali code of honor than an Iranian origin.
- Writing System: Persian adopted the Perso-Arabic script while Pashto uses a Perso-Arabic based script with additional letters for Pashto sounds.
This separation by geography and culture historically led the languages to drift apart through reduced contacts and adaptation to local environments over generations.
Preserving Shared Cultural Heritage
Despite becoming distinct languages, Persian and Pashto retain cultural and linguistic ties due to their shared Proto-Iranian roots. Many basic concepts, objects, family relations terminology are cognates across the two languages. Contemporary projects endeavor to celebrate this historical linguistic affinity. For instance, translated literary works between the languages help preserve interconnected poetic and storytelling traditions. Scholarship on comparative historical linguistics deepens understanding of language changes and cultural exchanges over the past millennia. Such research aids cultural appreciation and connections between Iranian peoples historically linked through their formative shared proto-language. Overall, while natural divergence shaped Persian and Pashto into distinct tongues, remembering their common ancestral origins fosters cross-cultural nuances important for regional cooperation and understanding between Iran and Afghanistan. Sustaining awareness of shared cultural heritage remains key.