The Importance of Farming Systems
Farming systems play a crucial role in addressing food security, livelihoods, sustainability and more. A well-designed system considers the complex interactions between agriculture, society and the environment to provide significant benefits.
Maximizing Efficiency through Integration
A farming system refers to the organized and integrated approach to agricultural production. By considering various components and practices working together, specific goals around food, socioeconomics and the environment can be achieved more effectively. Integration helps optimize resource use, minimizing waste and degradation. Land, water and nutrients are used in a balanced, efficient manner through crop rotations, integrated pest management and other techniques.
Systems Thinking Encourages Sustainability
Taking a systems approach encourages farmers to see their operations as interconnected with the broader landscape. This fosters sustainable land management practices like conservation tillage, cover crops and agroforestry systems. It also supports on-farm biodiversity through diverse crop varieties and habitat preservation. Well-designed systems utilize a range of crops, including traditional varieties suited to the region. This preserves cultural heritage while enhancing rural livelihoods.
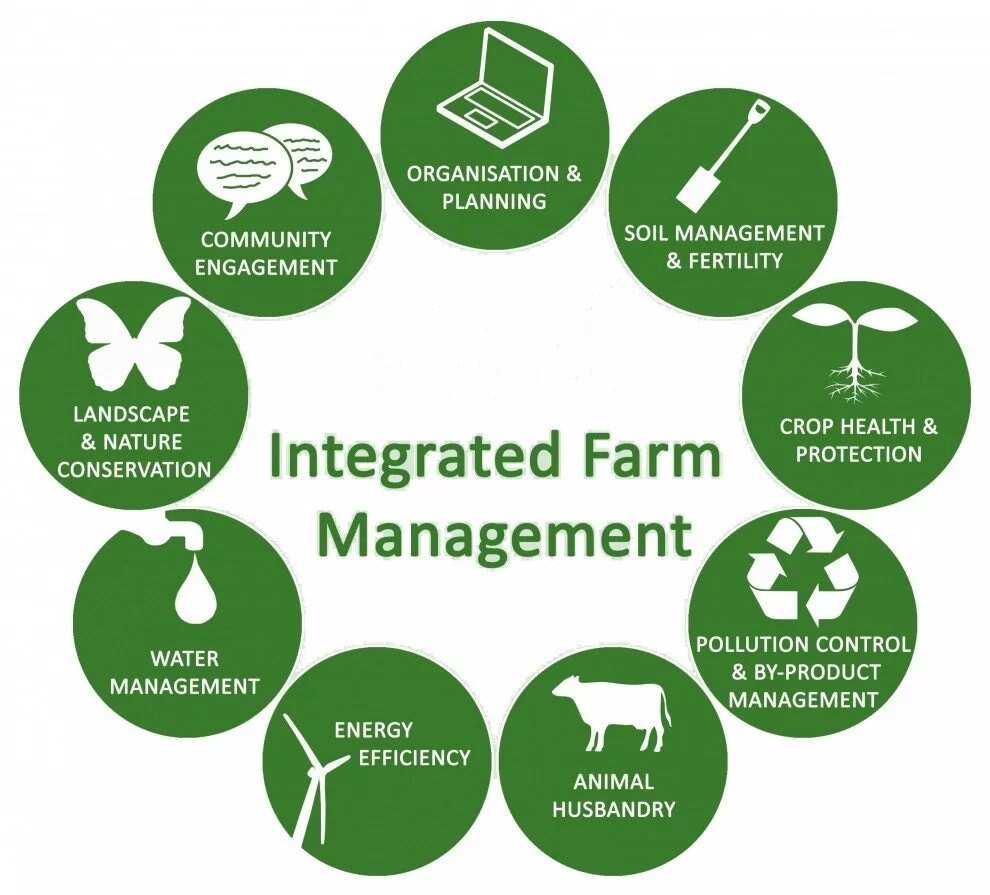
Providing Food Security and Economic Benefits
Farming systems play a vital role in global food production. By reliably supplying diverse agricultural goods, they support nutritional needs and help reduce scarcity issues. Staple grains provide a foundation for food security, while specialty crops offer dietary variety.
Supporting Rural Prosperity
Millions of livelihoods worldwide depend on farming systems. Employment is generated on-farm as well as in associated agribusinesses. Farmers gain income through crop and livestock sales. Rural communities benefit from the economic activity and infrastructure development spurred by agricultural production and trade. Exports also contribute valuable foreign earnings.
Building Climate Resilience
With climate change posing a serious threat, farming systems must adapt. Some incorporate practices like climate-smart agriculture using drought- and flood-tolerant varieties. Agroforestry and other techniques help sequester carbon from the atmosphere. Such resilient approaches will grow more vital for sustaining production under new conditions.
Fostering Innovation
Well-designed systems encourage continual improvement through farmer experimentation and collaboration with researchers. New technologies, like precision agriculture, boost productivity while reducing environmental impacts. Ongoing innovation will be key to further enhancing sustainability, resilience and other benefits into the future.
Conserving Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Thoughtful farm management can protect natural habitats and wildlife. Features like hedgerows, tree lines and wetlands support a diversity of pollinator and predator species. This biological pest control helps reduce reliance on agrochemicals. Certain grazing systems also aid land conservation by preventing degradation.
Communities and Cultural Heritage
Farming often brings people together and fosters strong rural social networks. Tasks from planting to harvest prompt cooperation among neighboring farms. Children also learn cultural traditions through involvement in agricultural activities. In this way, farming systems play an integral role in preserving cultural identity and heritage for future generations.
Conclusion
In summary, well-planned farming systems provide holistic solutions to challenges around food, the environment, livelihoods and more. Considering interactions between different sectors leads to smarter resource allocation and mutual gains. With sustainable practices and ongoing adaptation, these agricultural approaches will remain essential for communities worldwide - now and long into the future.
