Understanding Bitcoin Mining: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Bitcoon Mining Process
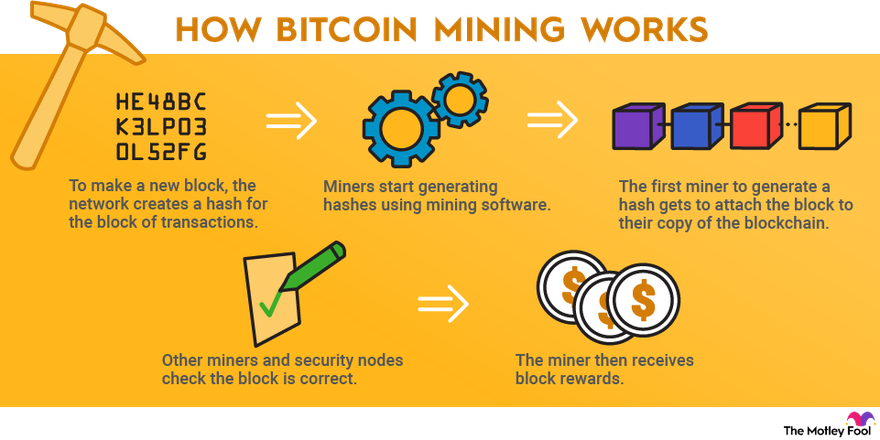
Block generation and verification
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new Bitcoin blocks are created and existing blocks are validated on the Bitcoin blockchain. Miners are rewarded with Bitcoin for securing the network through block generation and verification. To generate a new block, miners must solve complex cryptographic problems through an intensive trial-and-error process called “proof-of-work”. When a miner discovers the solution, they broadcast it to the Bitcoin network to be verified by other miners. Mining this new block allows the transactions within it to be confirmed and settled on the blockchain, creating operational security and immutability.
Mining hardware and performance
The type of hardware used for Bitcoin mining has a significant impact on mining profitability and performance. Miners use specially designed Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) that are specifically engineered to mine cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The computational power or “hashrate” of a mining rig determines how many hashes it can perform per second, directly affecting mining rewards.
Electricity costs are crucial
Bitcoin mining requires huge amounts of electricity to power high-powered ASIC miners, driving up operational costs. Miners pay close attention to electricity prices and typically seek locations with low-cost renewable energy sources. The rising costs of electricity over time means that older, less efficient mining hardware becomes unprofitable to operate.
Bitcoin Mining Rewards and Network Difficulty
Block rewards and mining subsidies
When a new block is mined, the miner generating that block receives a fixed reward of newly minted Bitcoins. The block reward is currently set at 6.25 BTC per block. This mining subsidy is halved approximately every 4 years to control the long-term rate of new Bitcoin issuance.
Dynamic difficulty adjustment
To keep block generation times at around 10 minutes on average, Bitcoin’s protocol automatically adjusts mining difficulty based on the total hashrate across the network. As more mining power joins, difficulty rises to maintain equilibrium - ensuring stability in the issuance of new coins. This protects the network from escalating too quickly or grinding to a halt.
Mining Pools and Cloud Mining Contracts
Mining pool collaborations
Individual mining is extremely challenging due to the immense computational resources required. Most miners joinlarge mining pools where collectively their hash power has a regular chance of solving blocks. Rewards are then shared among pool members proportionally based on their contributed hashrate.
Cloud mining and hosted services
Some miners opt for cloud mining contracts and hosted mining services. With these, miners pay an upfront fee or ongoing fees to lease mining hardware hosted at large data centers. Returns are based on the miner’s share holding and performance of the rented hardware. Reputable cloud mining providers ensure regular rewards over time.
The Future of Bitcoin Mining
Mining centralization concerns
While mining was originally decentralized among individuals, the rising costs and economies of scale have led to mining being dominated by a small number of large mining pools and firms. Some argue this poses centralization risks to the network. However, others believe mining incentives still entice geographic decentralization.
Alternative consensus mechanisms
With the energy costs of proof-of-work mining so high, many new cryptocurrencies are exploring alternative consensus mechanisms like proof-of-stake that don’t require specialized mining hardware. It remains to be seen if Bitcoin will transition in the long run. In the meantime, mining still provides critical security for the world’s largest blockchain network.
In conclusion, Bitcoin mining lies at the heart of how this decentralized digital currency works. By understanding the technical mining process, economic incentives, and evolving mining landscape, individuals can make informed choices on participating in securing the Bitcoin network through mining. Ongoing innovation will shape how this important function is performed into the future.
